Table of Contents
Do you all have a GitHub project that is no longer current or required? You would certainly look for ways how to delete the repository in GitHub? Deleting previous repositories (repos) needs to clean up your profile for future employers looking at your software. If you’re the owner of the organization or have admin capabilities, you can delete a repository at any moment. Whenever a repo is erased, it is sometimes possible to recover it under certain circumstances.
Even if you can retrieve a repo, there are still a few significant ramifications when you delete it. For example, when you delete a private repository, you also erase all branches (online copies). If you deactivate a public repo, however, the forks will remain.
If a repo is made public and then made private, the forks made while the public repository will not be erased. You choose whether you want the storage to be shared or personal when you create it, but remember that even if you change the repository to private and then delete it, some information may still be available to the public. Any problems, documents, team privileges, and comments related to a repository will also be deleted. If you think you’ll need to refer to some of this content in the future, don’t delete the warehouse because it’s irreversible.
How to delete the repository in Github?
Before we go deep into knowing how to delete the repository in GitHub, you have to visit the GitHub webpage in your preferred browser and sign in to your profile if you’re sure you want to remove your repository. Then, choose the “Repositories” group in the left-hand pane and select the repo you want to delete. Under the repo’s metrics, click the “Settings” button.
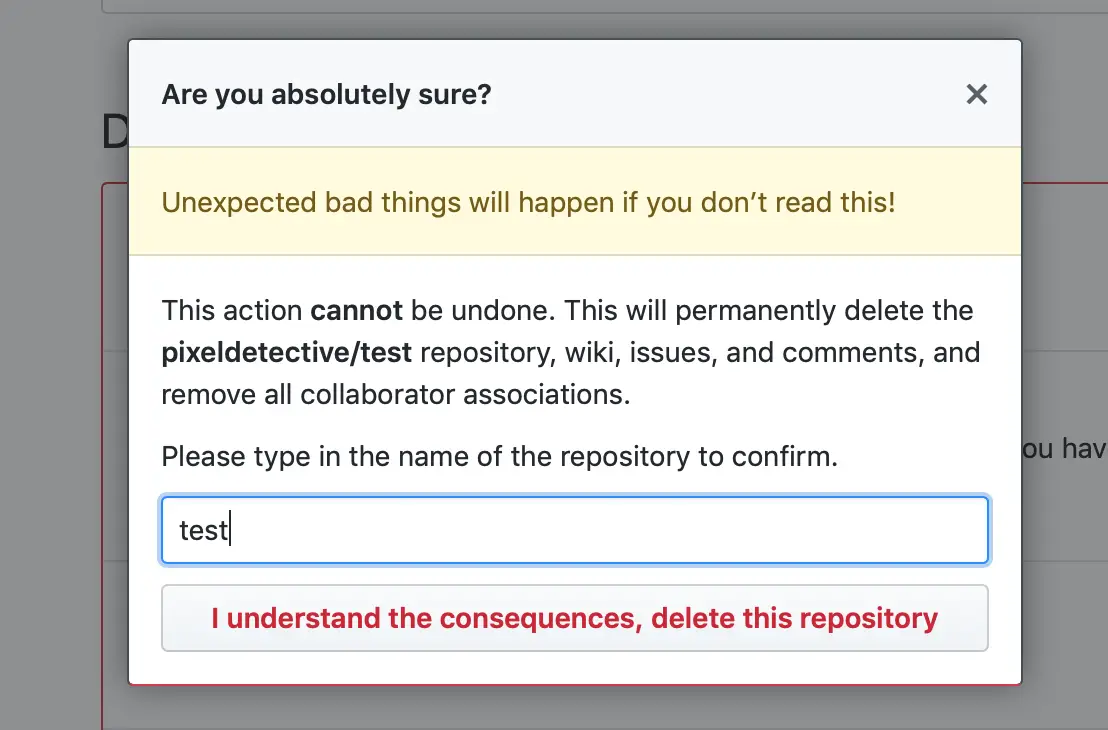
Now scroll down to the Danger Zone area at the end of the Settings page. Select “Delete This Repository” from the drop-down menu. A pop-up box will display, informing you that the operation is permanent and asking you to confirm by typing the repo name. Read the caution carefully, type your repository’s name into the text box, and then select “I understand the consequences, remove this repository” from the drop-down menu.
If you’re the organization owner or have the admin capabilities for that repo or fork, you can delete it. However, there are some factors to keep in mind when you search –how to delete the repository in GitHub:
The upstream repository is unaffected by the deletion of a fork. For example, a private repository’s forks will be deleted if it is deleted, but a public repository’s forks will not be affected.
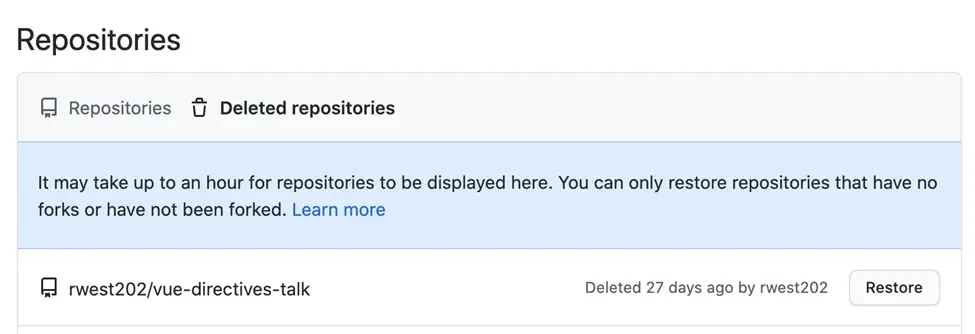
All wikis, problems, and comments related to a repository will be deleted if it is deleted. A repository cannot be restored once it has been destroyed. So don’t try to claim that we didn’t alert you.
You might consider archiving the repo instead of deleting all data if you’re not confident about deleting everything. Select “Archives this repository from the very same Danger Zone section.” The storage will be set to read-only, but some other customers will always be able to clone it. You can always return to the repository’s preferences page and click Unarchive your repository to resurrect it. You’ll be taken back to the GitHub home page after deleting the repository, with a banner at the top indicating that the repository was deleted correctly.
There isn’t a trick to deleting a Github repository directly from your computer. All that you need to do is- delete everything from the folder where the Github repository either was cloned or initialized. That is all there is to it.
How to delete the repository in GitHub: Is it possible to delete the Github repository?
Okay, there might be a ruse here. The DVCS tool keeps most of its configuration items in a secret subdirectory of GitHub in every GitHub repo. Attempts to delete a GitHub repository locally will fail if your computer isn’t set up to expose concealed files and folders because they are hidden. Git folder will remain. Configure your machine to show local folders, and then delete them. You can use the Git folder using File Explorer on your operating system to remove the local Git repository.
You can delete a Git repository from the command line if you’re comfortable with the command prompt or the DOS prompt. To recursively remove the Git folder and all of its files and folders, using the rm program with the -f and -r switches. When you search for how to delete the repository in GitHub, you can also use this GitHub repo deletion command to destroy the GitHub repo while leaving all other files and folders alone.
When you use the Github BASH terminal windows to delete the Git repository, you’ll see that the current Git branch’s name is no longer listed after using the Git removal command. As a result, any Git queries you run will result in a catastrophic: not a GitHub repo error. While we don’t usually look for confirmation in software development work through failures, in this situation, seeing this devastating mistake is proof that the private Github repository removal procedure was successful.

In GIT, repositories are collections of files and data from different iterations of a Project. These documents are transferred from the repo into the user’s local server for additional updates and changes to the file’s content.
A VCS (Version Control System) is utilized. Cloning is transferring data from a current Github Repository with various Git Tools. The customers receive the entire repository on their PC after the cloning operation. Once the replication is complete, Git assumes that all work on the repository will be done as a user.
While learning how to delete the repository in GitHub, you will find a working tree that works as a collection of files and data originating from a specific version of the archive. It aids in tracking modifications made by a particular user in a specific version of the repository. When a user commits to an action, Git only looks for the files available in the workplace, not all updated files. Therefore, the commit operation only considers files available in the working area. The owner of a working tree can modify files and remove or create new ones.
A GIT repository can build multiple variations of a project by executing different operations. Files and data can be added, new repositories can be created, actions can be committed, repositories can be deleted, etc., when you search how to delete the repository in GitHub. As a result of these changes, separate copies of a project will be created. After making changes to a file in the Work Place, GIT must take two further steps to save the impact on the local repository.
These are the steps:
- Making the necessary adjustments to the Index (Staging Area)
- Adding the indexed changes to the repository and committing them
Git allows users to replicate repositories on their machines and conduct their operations. As a result, many separate versions of the project will be created. This won’t integrate their modifications with other developers because these copies are saved on the local machine. Git allows the local repositories to be synced with remote repositories to solve this difficulty.
Things to know when you learn how to delete the repository in GitHub: The two Git Commands?
This synchronization may be accomplished with the help of two Git commands. These are the commands:
Push: This command pushes all of the current repository’s commits to the monitored remote repository. You can use this command to push the repo to many repositories simultaneously.
Pull: The pull command pulls contributions from a local repository and saves them in remote branches. Other users may change their copies of repositories and then upload them to other distant repositories. However, your repository copy will seem to be out of date in that situation. As a result, to re-synchronize the repo composition with the temp folder, use the Git pull instruction to acquire the remote repository’s content.
What are the types of Git repositories?
Based on user rights, there are two main types of Git repositories:
- Repositories with No Content
To exchange adjustments done by team members, software developers use bare repositories. Individual users are not permitted to change the repository or create new versions.
- Repositories That Aren’t Bare
Users can edit existing repositories and develop new versions using non-bare repositories. The cloning method provides a non-repository by default.
How can you use the repository?
- Repositories can be used to organize your work and communicate with others.
- Issues can gather customer input, report software flaws, and organize activities to be completed.
- You can use GitHub Forums to collect more information, exchange data, make announcements, and start or join project discussions.
- Pull requests are a way to propose modifications to a repository.
- Project boards can be used to organize and prioritize problems and pull requests.
Conclusion
You can grant collaborator access to other people in user-owned repositories so that they can work on your project. In addition, if an organization controls a repository, you can grant access permissions to members of that organization to collaborate on it.
You can work with an unlimited number of collaborators on a complete range of public repositories with a full set of features, or a total number of private repositories with just a limited feature set, with GitHub Free for user-profiles and organizations. However, when you search for how to delete the repository in GitHub, you must be very careful with the process mentioned above.
Deleting unnecessary data is essential to make full use of your storage capacity. We may also require deleting a social media account when we no longer use it. However, there are situations when we are not well aware of the proper deleting methods. This blog on 6 Simple Methods Of How to Delete Roblox account will guide you to delete your Roblox account.

