Cough After Eating- Causes, Dietary Modifications, And More.
Have you been getting a cough after eating too often these days? You barely finish a tasty meal with your family, and then it starts: coughing after eating. This unusual cough may happen periodically, or some people begin coughing after each meal at any time of the day.
Mostly, coughing is an indication of an underlying ailment. The body is reacting to discomfort in your throat. So, the most reliable means to mitigate the cough is by dealing with the underlying reason.
What results in cough after eating? Here are some things you want to understand about cough after eating.
Clearing Irritants from your Respiratory System
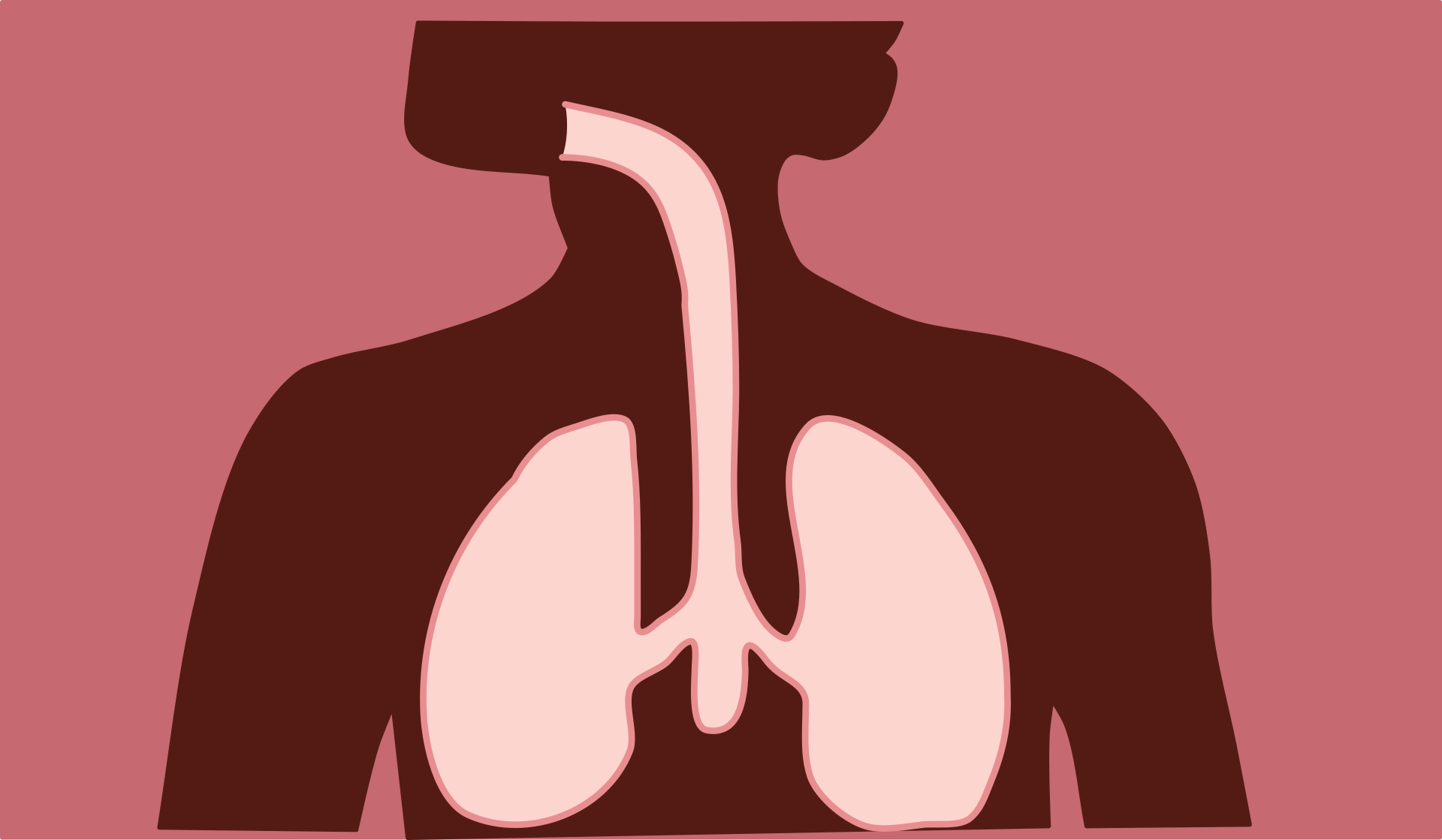
Coughing is a response that happens when the body grasps irritants that require to be kept out of your respiratory system. For instance, if food components or phlegm stucks within the throat, your body will begin a cough to stride these undesirable things out of your respiratory area.
In most circumstances, cough after eating can be averted by shifting your diet, eating patterns, or medication. The most reliable solution is to discuss with a doctor for a diagnosis. Then, you can put together the lifestyle modifications required to deal with these underlying reasons.
Before discussing more- cough after eating, let’s see the difference between chronic cough and cough fits.
Coughing Fits vs. Chronic Coughing
Everyone undergoes it now and then when water or food “goes below in the wrong pipe.” This incident results in an unexpected, tough coughing fit. But this coughing will quit when the throat is cleaned again.
Gulping food or water incorrectly should not be an everyday experience. If it occurs frequently, you may need to talk to a specialist to see if there are underlying ailments that contribute to the issue.
If the coughing occurs after you are finished eating, then it may be an indication of another problem. It is crucial to report the timing of your cough, as well as any foods that may be adding to the cough.
Here are a few underlying causes of cough after eating to note down.
Causes Of Cough After Eating
1. Acid reflux and related ailments

Acid reflux arises when stomach acid progresses back up to the esophagus. There is a band of muscle near the bottom of the esophagus known as the lower esophageal sphincter. When you consume food and drinks, it loosens, enabling food and juice to move within the stomach. Sometimes it does not entirely close when you are done eating or drinking, enabling acid from the stomach to move upward into the esophagus. This irritates the esophagus, which might cause you to start coughing after eating.
Additional symptoms of acid reflux are:
- sore throat
- bitter flavor in the back of the throat
- sour flavor within the mouth
- burning feeling in the chest, called heartburn
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
GERD is a continuous, more severe pattern of acid reflux. A chronic cough, particularly after consuming food, is a widespread symptom.
Other indications of GERD comprise:
- having acid reflux twice a week
- Belching
- nausea or vomiting
- Wheezing
- trouble swallowing
Laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR)
LPR, also known as silent reflux, doesn’t possess conventional reflux signs. It is a category of GERD that includes stomach acid passing via the esophagus and into the larynx or straight to your nose. You can have LPR with GERD or without GERD. LPR can cause a cough after eating or during eating. You may also cough when you wake up, talk, or laugh.
Signs of LPR comprise:
- hoarseness
- continually wanting to clear the throat
- the sensation of a thing trickling down the back of the throat from your nose, known as postnasal drip.
Speak to the doctor if you possess any LPR signs. LPR, when left untreated, might ultimately cause voice diseases or throat ulcers, so timely treatment is crucial.
There isn’t a remedy for acid reflux, LPR, or GERD, but particular pills and home treatments can enable you to govern the symptoms.
2. Respiratory infections

Many coughs result from upper respiratory infections, but such coughs usually clear up within a few weeks. Any cough remaining eight weeks and longer is supposed to be chronic. A chronic cough after eating may result from any prior infection that never recovered properly.
A cough induced by an infection creak like a dry, harsh, persistent hack. This cough results in inflammation in the airway, which may cause extra coughing.
Coughs inflicted by infections are hard to deal with because the progression of inflammation and coughing hinders healing. If the cough is not cured, your doctor might suggest anti-inflammatory medication, such as oral or inhaled steroids.
3. Asthma

Asthma is a severe, lasting disease that influences the lungs. It can result in wheezing, coughing, and chest tightness. Asthma typically begins in childhood, but it can also happen when you get older. Coughing resulting from asthma usually is worse early in the morning or late at night.
The signs of asthma become worse during an asthma attack. Many things can accelerate an asthma attack, comprising sulfites, which are found in wine and beer, dried vegetables and fruits, pickled onions, and sweet drinks. If you are inclined to cough after eating any given, asthma may be the possible cause.
You can always effortlessly manage asthma with some drugs and avoid widespread asthma triggers.
4. Food allergies

Food allergies typically formulate when you are a kid, but they can attack at any age. It is even feasible to evolve an allergy to a food you have been otherwise eating for years. Food allergies commonly spur an allergic reaction within one to two hours of eating.
Allergic response indications differ from one person to another, and they periodically influence the respiratory system, resulting in you coughing. Additional respiratory indications of a food allergy encompass shortness of breath and wheezing.
In unusual cases, food allergies may also cause anaphylaxis, a life-threatening ailment that influences your breathing. Ensure that you know how to comprehend it to achieve timely treatment.
5. Cough After Eating Due To Dysphagia
Dysphagia means having complications swallowing food. If you possess dysphagia, your body needs more time and endeavor to shift food or liquid into the stomach, making gulping uncomfortable or almost unthinkable. This may lead to coughing or choking while swallowing. Dysphagia can furthermore make it feel like you have anything glued in your throat, resulting in you coughing.
Many circumstances result in dysphagia, comprising acid reflux and GERD. Talk to your doctor to find out what is causing the dysphagia. Periodically simple workouts are sufficient to rectify the problem. In more severe cases, you might require surgery or endoscopic procedure.
6. Aspiration pneumonia
At times tiny pieces of food or a few drops of liquid get inhaled within your lungs, where they may bring up bacteria. This occurs typically when you gulp something and it “gets down the incorrect hole.” Healthy lungs commonly empty themselves, but if lungs do not, such bacteria can result in a severe ailment known as aspiration pneumonia. Getting acid reflux or dysphagia boosts your chance of formulating aspiration pneumonia.
A wet cough after eating is a sign of aspiration pneumonia. You might furthermore cough up mucus that appears bloody or green. Additional symptoms are:
- uncomfortable swallowing
- Wheezing or cough after eating
- heartburn
- fever that begins within one hour of eating anything
- pneumonia that reoccurs
- excess saliva
- congestion after drinking or gulping food
- fatigue or shortness of breath while or after eating and drinking
If left without treatment, aspiration pneumonia can result in severe difficulties, such as respiratory failure or lung abscess. Speak with your doctor as soon as you can if you believe you may have developed aspiration pneumonia.
7. Cough After Eating Due To Chronic Laryngitis
Laryngitis results in inflammation within the vocal cords, and you might have a hoarse, irritating voice or raw-feeling throat and complications swallowing food. These signs cause frequent coughing, and such cough is the dry one, often known as smoker’s cough.
Prevention is the answer to halting your severe coughing from this laryngitis. This ailment results from excessive drinking or smoking, which is frequently incorporated with long nights out, partying, and screaming. These actions aggravate your throat and can lead to chronic coughing in LA. If you feel fine besides your coughing, you are likely suffering from chronic laryngitis.
Dietary Changes to Prevent Cough After Eating

If coughing repeatedly occurs after eating, you may need to attempt dietary modifications to lessen the symptoms. Try these variations in your diet:
1. Avoid Phlegm-Causing Foods
Particular food categories can result in the phlegm rating you eat, like dairy products. A few people retain sensitivity to cream, cheese, and milk.
The body may boost the generation of phlegm, which heightens the probability of coughing after you eat. Averting dairy elements may assist in governing the coughing.
2. Spicy Foods
Spice can add to acid reflux, which is why the coughing may be more frequent after you eat a spicy meal. Typical culprits comprise got sauce and peppers.
If you are diagnosed with GERD or acid reflux, then obey the doctor’s suggestion to lessen foods that add to these ailments. It can furthermore be helpful to use medicines as prescribed by the doctor.
3. Citrus and Acetic Acid
A handful of components tickle the cough center and may cause cough after eating. Pay awareness to the coughing symptoms after consuming citrus foods, such as limes, oranges, lemons, or grapefruit. Acetic acid (usually discovered in vinegar and pickled vegetables) can result in a related result.
When coughing rises after eating such foods, you may need to lessen them or eradicate them from the diet.
4. Eating Habits
You can also lessen the likelihood of cough after eating by modifying your eating patterns. Here are some recommendations to check out:
- Overeating can boost the danger of acid reflux, so you must be more active in controlling quantity or portion sizes.
- Eat unhurriedly and munch well before gulping
- Sit up upright and prevent eating when you are lying down
- Take tiny sips of water between every bite.
- Maintain a food diary to note the eating patterns that boost the chance of coughing after you eat the meal
- Do not consume anything during a coughing fit.
- Take prescriptions as proposed by your doctor for acid reflux or asthma.
Consulting with a Doctor about Chronic Coughing
As you can read above, numerous factors could add to the chance of coughing after you have the meal. Many of such causes are simple to govern or treat. It would help if you spoke to a doctor to discover the underlying reason for the coughing fits.
The bottom line
Various things can give rise to cough after eating, and many of them are simple to deal with or manage. Keep trail of any extra signs you have and speak with the doctor to determine the underlying reason for your condition.

