Table of Contents
If you have never heard about the Toulouse-Lautrec syndrome then it might sound like a very serious thing to you. Well, I am here to clear any doubts that you might have regarding this syndrome and tell you everything you need to know about this syndrome.
Toulouse-Lautrec syndrome is a very rare genetic condition. It affects about one person in 1.7 million people worldwide, and in literature, there have only been 200 cases that have been described which is just 5% of the total number of cases.
Toulouse-Lautrec syndrome is named after a famous French artist who used to live in the 19th century. His name was Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec. It is believed that he had this disorder as well. Clinically, this syndrome has another weird name called pycnodysostosis or pyknodysostosis (PYCD). At least the abbreviated form is memorable, phew!
PYCD is probably best known as the diagnosis given retrospectively to Toulouse-Lautrec, who Jose Ferrer also portrayed in the movie Moulin Rouge that came out in 1952. PYCD is a syndrome that causes brittle bones in the body and other things like abnormalities of the face, hands, and some other body parts.
Toulouse-Lautrec syndrome is a genetically inherited disease, and the pattern of inheritance follows the classic rules of genetics. I will be explaining that a bit more below. This syndrome can cause a lot of abnormalities in the body, both exterior and interior.
In this article, we will discuss what the Toulouse-Lautrec syndrome is, why it is named pycnodysostosis, the characteristics of this syndrome, the risks associated with it, and how it gets inherited, its causes as well as its symptoms, and some other facts about it. So let us start on the journey to understanding this disease.
What Is The Toulouse-Lautrec Syndrome?
As mentioned above, the Toulouse-Lautrec syndrome is a genetically inherited disease known to make the bones brittle and give you some other deformities in the face or hands. PYCD can cause short stature. The height of adult males would not go above 150 cm or 5 feet, and when it comes to adult females, their heights get even shorter.
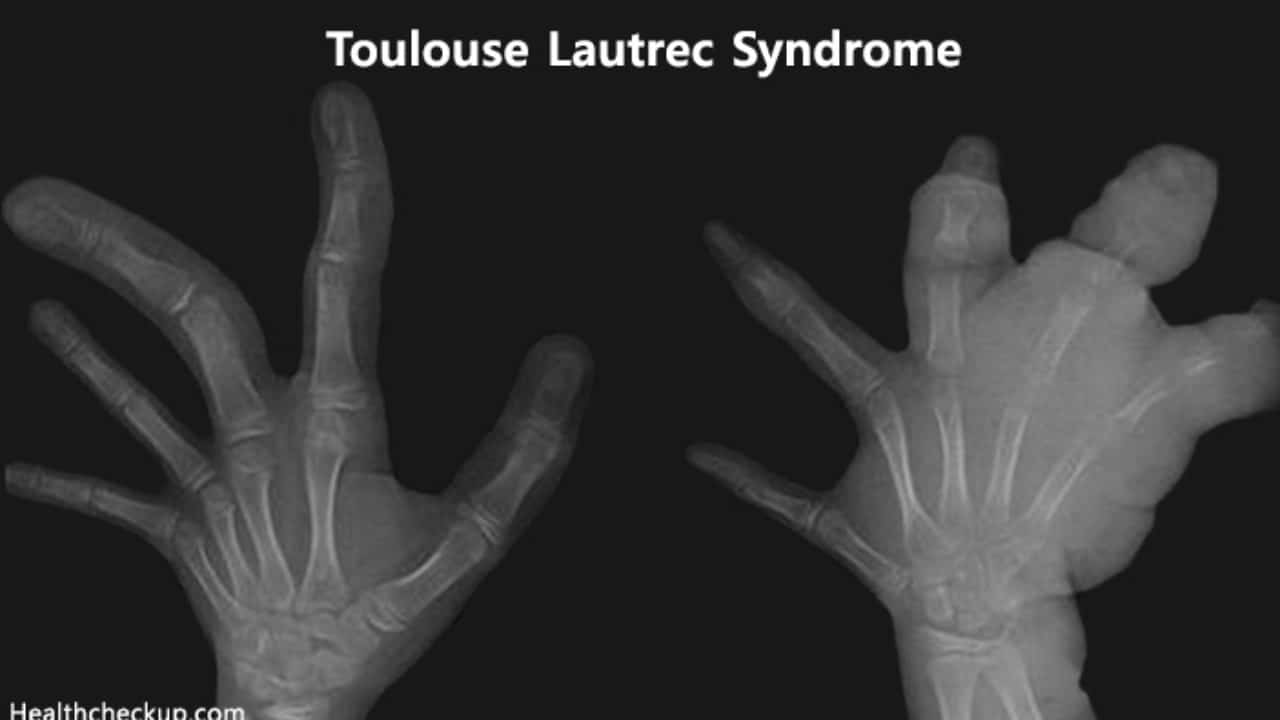
Toulouse-Lautrec syndrome causes the bones to get abnormally dense, leading to a condition called osteosclerosis. It also makes the last bones of the fingers, i.e. the distal phalanges, no, not Regina Phalange, you nerd, very short.
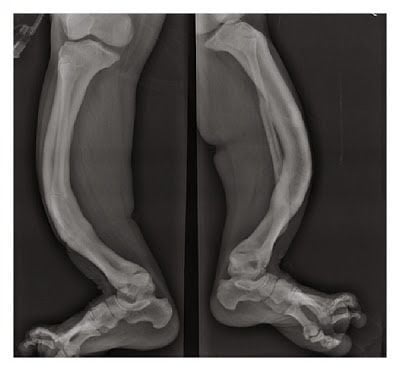
It also causes a delay in the normal closure of the connection of the skull that is called sutures during infancy. So that is why, the soft spot or the fontanel, which is on the top of your head, remains wide open. Having brittle bones exposes them to getting fractured very easily. The bones in the legs and feet are more prone to fracturing than any other bones in the body.
After the leg and foot bones, the collar bone or the clavicles are very easily fracturable as well. The precise frequency of the Toulouse-Lautrec syndrome has never been determined. PYCD can be classified into large groups of genetic diseases that are individually not very common but are collectively very important because of their sum of numbers.
They are also very significant because of the heavy impact that they have on an individual and of course, the heavy burden that falls on the family of the affected person. All in all, it is not a fun syndrome to have.
Talking about the name of the disease, pycnodysostosis, it originated from the French physicians Maroteaux and Lamy in 1962 when they described it as ‘La pycondysostose’ in their report. You should note that these physicians were not the only discoverers of this disease. Andren and his colleagues also described this condition in the same year.
Maroteaux and Lamy put the ‘pyknos’ in the name as it means dense in Greek and added it to the compound word ‘dysostosis’ which means abnormal bone formation and hence, the name shows that this is a disease that causes dense bones. A variation of the name is used in certain places where they use ‘k’ instead of ‘c’ in pycnodysostosis and spell it as pyknodysostosis.
Characteristics Of The Toulouse-Lautrec Syndrome
PYCD causes a lot of abnormalities in the body even if you exclude the brittle bones or short stature or short fingers and wide soft spot on the skull. These other abnormalities involve the head and face, the teeth, collar bones, skin, nails, etc.
Mostly the front and back of the head are prominent. Inside the open sutures of the skull, there are a lot of tiny bones which are known as the wormian bones. It also makes the mid-face, less full than usual. Your nose becomes prominent, the jaw can be smaller.
The palate can be narrow and grooved, the baby teeth would come in late and they might get lost much later than usual for a baby. The permanent teeth could appear late or be slow to appear and might be irregular or some teeth might even be missing, something that is called hypodontia.
The collar bones often are found to be not developed completely and be malformed. The skin over the back of the fingers are very wrinkled and the nails are flat and grooved as well. The Toulouse-Lautrec syndrome also causes some issues that will make themselves known with time.
Other than the broken bones, the distal phalanges and the collar bones can undergo a very slow but progressive deterioration. It might cause some defects in the vertebral column resulting in a curved spine and scoliosis. All the tooth problems would need professional help and some cavities might form over time as well, those are pretty common in this condition.
Other characteristics or symptoms include:
- High forehead
- Abnormal fingers
- Short toes
- Enlarged liver
- Difficulty with mental processes (Intelligence does not get affected usually)
- The narrow roof of the mouth
- Short stature with adult-sze trunk and short legs
- Breathing patterns are not normal
People with this disease will have to be careful of not falling or fracturing their bones as the healing process is a bit harder for them. They could have mobility issues later and it will prevent them from exercising and can also affect their weight and cardiovascular fitness. Overall, this disease can be a pain in the backside. No! Not literally! Gosh.
What Causes The Toulouse-Lautrec Syndrome?
The Toulouse-Lautrec syndrome is caused by the mutation of the gene that codes the enzyme cathepsin K (CTSK) on chromosome 1q21. Cathepsin K is something that helps in bone remodeling as it breaks down the collagen which is a protein that acts as a scaffolding to support the minerals such as calcium and phosphate in everyone’s bones.
PYCD is something that is categorized as an autosomal recessive disorder which means that a person must be born with 2 copies of an abnormal gene for the disease or the physical traits to develop. Genes are something that gets passed down in pairs, of which you get 1 from your dad and 1 from your mom.
Suppose if both the parents have 1 mutated gene then they will become carriers of it. Here are the chances and how a person can develop the PYCD:
- Suppose if the kid gets one mutated gene from a parent and the other parent’s genes are not mutated, then they would become carriers as well. In such a case, they have a fifty percent chance of developing this disease.
- Suppose if the kid gets mutated genes from both of its parents then their chances of having this disease will be at 50%.
- If the kid inherits unmutated genes from both its parents then they will not become carriers and they might not have the disease either. They will only have a 50% chance of getting it.
Does that all sound confusing? Don’t worry, I will explain it in the next heading. PYCD is autosomal because the genes for PYCD are situated on one of the non-sex chromosomes (autosomes).
It is recessive because just one edition of a PYCD gene would, in most cases, not be enough for you to get this disease. You must have two copies of the abnormal genes in you for you to get this disease.
What Risks Does The Toulouse-Lautrec Syndrome Pose?
Toulouse-Lautrec syndrome is a very rare disease. If anyone in your family has not had this disease then the chances of you getting it would be super low. Although, if you are a child born from a consanguineous union, that if you are the result of inbreeding or incest, then you will have a greater risk of getting this disease.
If one of your parents has a rare gene that can give the Toulouse-Lautrec syndrome, then there might be chances that their spouse, to whom they are related, would also have the same gene. And if that is the case then the risk of you getting PYCD will increase tenfold.
Like I said if you have someone in your family with PYCD, you will have a greater risk of having this disease as well. You should keep in mind that the parents of a child that has Toulouse-Lautrec syndrome might not have the disease themselves, they will just be the carriers of this gene.
Each parent has half a chance of transmitting this disease to their child. You could consider it like tossing a coin because you will have half a chance of getting it from either parent, so you will have a 50% chance of getting the disease. Every child would have at least a 50% chance of getting this disease if at least one of their parents is carrying the mutated gene.
Diagnosis
Toulouse-Lautrec syndrome is diagnosed in infancy. Although, as this is a very rare disease, it might not get diagnosed when you are a kid at all or the physician might make a wrong diagnosis too.
To diagnose this disease properly, physical exams along with health checkups and the medical history, everything is taken into account. If you are able to acquire the family’s vague medical history, just that might be very helpful as well because if the Toulouse-Lautrec syndrome gene is present in any other family member, then it will help the doctor make the diagnosis faster.
X-rays are very helpful in identifying this disease as well because they show the bone structure and the images can show the characteristics of the bone that have the PYCD symptoms. Molecular genetic testing can help in confirming the diagnosis as well.
To make sure the molecular genetic testing is done properly, the doctor needs to know to test for the CTSK gene as well. Testing for the gene is done at specialized laboratories and that is because it is a very rarely performed genetic test.
Treatment Options Available To You
For treating the Toulouse-Lautrec syndrome, specialists are required. The child with PYCD will have a healthcare team that will have a paediatrician, an orthopedist, which is a bone specialist, and possibly an orthopaedic surgeon as well as an endocrinologist which is a doctor specializing in hormonal disorders.
PYCD might not be a hormonal disease but some hormonal treatments help with certain symptoms. Every Toulouse-Lautrec syndrome treatment has to be designed specifically for the individual.
If the roof of your mouth is narrowed then a dentist, orthodontist, and maybe an oral surgeon would be required to take care of your teeth health. If you have any facial deformities, then a cosmetic surgeon might be asked to help.
The care you receive from an orthopedist and orthopaedic surgeons would be very significant throughout your life. If you have Toulouse-Lautrec syndrome, then that might mean that you would have a lot of fractures as well including stress fractures that developed over time. Some people diagnosed with it might even need rods placed in both their legs.
People diagnosed with PYCD could have short stature and hence an endocrinologist can come into play as they will monitor your growth hormones. Some manipulations of certain genetic functions could also be done to help you. A tool known as the Clustered Regularly Interspaced Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) is used for that.
Cessation
Toulouse-Lautrec syndrome is a very rare disease but what you should know is that you can be helped to overcome the symptoms of this disease. This disease does not have to be fatal. Although, you might have to make certain adjustments to your lifestyle.
If you are carrying a PYCD gene or if you have this disease then you should take advice from professionals before you make a decision on whether to have a child or not. You should get your partner or spouse tested for this gene too because both of you having it might increase the risk of your child having it. Just keep in mind that like every other disease, this can be overcome too.

