Table of Contents
Heel Pad Syndrome- Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, And Prevention Tips!
Heel pad syndrome is a condition that occurs when changes happen in the overall elasticity and depth of the heel pad. It is mainly caused by wear and tear of muscle fibers and fatty tissues that damages the cushioned pad on your feet’s sole.
Your feet are the most distal part of the human body. Principally, the role of your feet is to balance your body posture, spreading the body mass to the ground without placing too much stress on your inner tissues, and supporting the movement.
Here is all you need to learn about heel pad syndrome causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment.
Heel pads and heel pad syndrome

The heel is formed of thick tissue layers inside the soles. It is the build-up of dense fat pockets enclosed by tough and stretchy muscle fibers.
Whenever you run, walk, or jump, the heels pads function as cushions to distribute the body weight and absorb shock, thus protecting the joints and bones from injuries.
You might not realize it, but the heels endure too much. Due to this, it is quite normal for them to wear down over time. They wear down a bit not completely. However, wearing your heel pads too much can cause the heels to shrink over time and lose elasticity. If this occurs, they no longer remain capable of absorbing shocks and this condition is what we describe as heel pad syndrome.
If you have heel pad syndrome, you will have difficulty with everyday activities like standing, talking, running, etc. It will trigger pain, inflammation, and tenderness in one or both heels.
Risk Factors and Causes of the heel pad syndrome
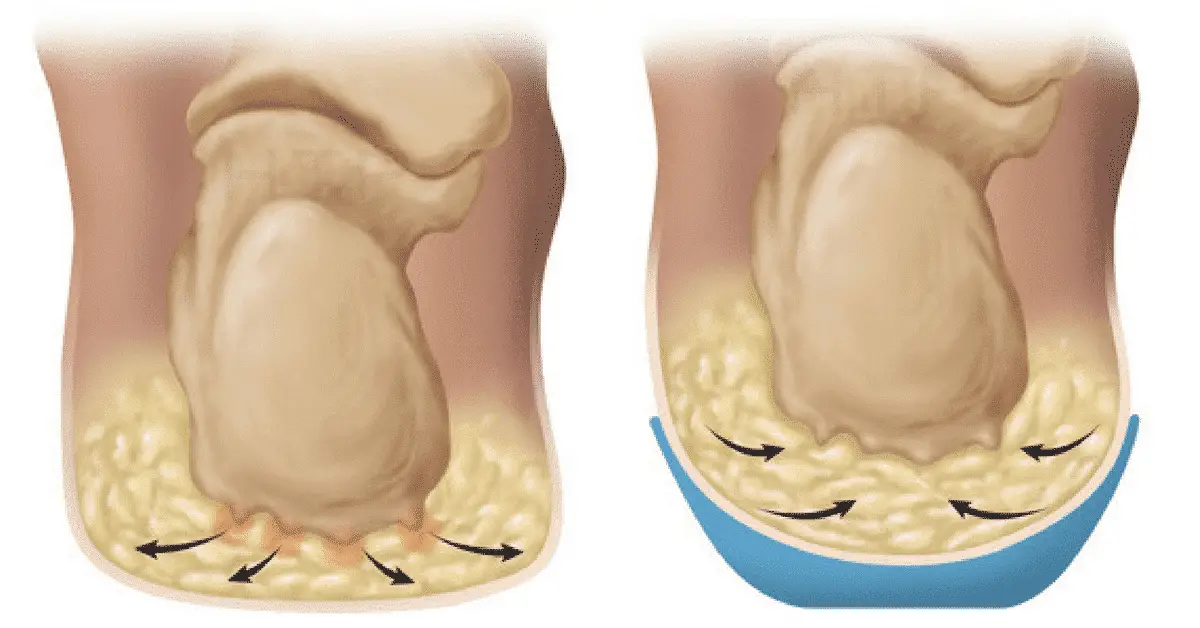
Various factors are involved in the development of heel pad syndrome. Sometimes, this condition might be caused by several factors, these factors are:
1. Aging Process
As age progresses, several important systems in our body go through a process called degeneration. In this process, our systems grow less active. This involves not only vital systems of our body but also includes the soft tissues of the body.
The aging method influences the heel pad’s soft tissues and the fat layer, thus lowering its elasticity and thickness. As we age and with more extended use of feet, often above age 40, the fatty coating in the tissue beneath the skin begins to disrupt with it.
Muscle tissues and collagen fibers are also lost. When the cushion beneath the legs diminishes, it is obvious that the shock-absorbing property of our feet will also lessen and we will be highly susceptible to injuries and bruising of the heel bone, causing pain.
2. Sudden trauma or injury
Any trauma or injury within our heel pad also causes heel pad syndrome. This injury may be due to accidents, games, or high-level workouts that damage the heel pads.
3. Obesity
It is quite easy to estimate that the more your body weight is, the more pressure or stress will be placed on your heel pads. This will in turn decrease the flexibility of heel muscles and your heel pad.
4. General issues with the structure of the body and gait
Oftentimes, the problems with gait and general structure of your ankle joint, hip joint, knees, and feet can also change the pattern of your walking because of unequal weight distribution across the feet. This results in a major injury and deformity of the heel pads resulting in heel pad syndrome.
5. Inappropriate footwear
You may take it very lightly but wearing improper shoes or footwear for a long time is not good for your feet especially if you are performing activities or weight exercises. This may add to losing of tensile strength within your heel pads.
6. Tough and rigid surfaces
If you are more prone to running or walking on hard surfaces, this may lead to stiffness in your heel pad. Even if the muscles inside the heel pad are not lost, they may still lose some of their capability to absorb shock due to the rigid surface.
7. Tiresome activities
If you keep performing repeated activities which make you feel tired like running, jogging, or jumping repeatedly, it may cause chronic changes in your heel muscles thus leading to inflammation and loss of strength in the heel pads.
8. Plantar fasciitis
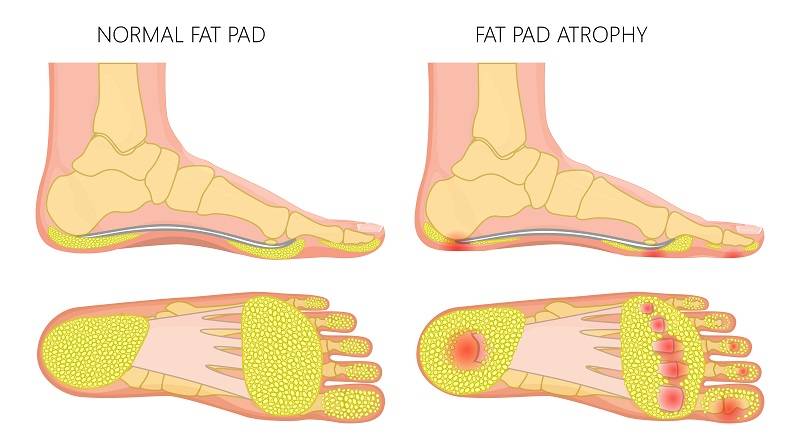
Degeneration in the plantar fascia takes away the ability of absorbing shocks or supporting your feet. This might cause more stress on your heels and cause heel pad syndrome.
9. Corticosteroid injections
Injections of corticosteroids might also cause a gradual decline in strength inside the muscle of the heel pad rather than reducing inflammation and pain. This may occur as a result of the side effects of using corticosteroid injection.
10. High arched feet
People having high arched feet who are involved in numerous activities like sprinting, running, or other high-level names are more prone to getting heel pad syndrome due to improper movement of the fat layer within the heel.
11. Genetics in family related to heel pad syndrome
If your family has a previous history of this condition, it may also result in causing heel pad syndrome or degeneration of muscles.
12. Additional conditions
There are a few other health conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes mellitus, and lupus that are linked with the development of heel pad syndrome due to the loss of collagen fibers and adipose tissue in the heel region. Moreover, diabetic patients are prone to suffering from the loss of peripheral nerves supply toward feet and legs or peripheral neuropathy.
This results in misplacing some of the sensations of the nerve. Due to this a person is not able to feel the pain and puts extra pressure on the heel thus leading to permanent damage or injury in the heel pad tissues. This is one more cause of heel pad syndrome.
Other potential causes are:
- A pinched nerve.
- Haglund’s deformity
- Bruised heel
- Planters warts
- Tumor
- Tendinopathy
- Tarsal runner syndrome
Now, if you have developed heel pad syndrome, how to find out? Below given are a few symptoms to consider:
Symptoms of heel pad syndrome
If you are suffering from heel pad syndrome, you are most likely to see some of these symptoms. Common symptoms are:
- Deep pain in your heels, mainly in the middle of the calcaneal bone, causing pain around the heel pads.
- The pain feels like an injury or internal bruise in the sole during running, walking, standing, or jumping.
- When you press or tap the heel, you will feel such pain again.
- The intensity of this pain keeps increasing as you perform activities of walking, jumping, or running especially without wearing anything.
- In severe cases, a person cannot walk or even stand due to high-intensity pain in their sole.
Few less commonly viewed symptoms are also there, and you may or may not feel them. These include a cold, burning, or prickly sensation inside your heel due to neurological ailments in nerves nearby, located superficially after fat atrophy and muscles in your heel pad.
Minor cases of heel pad syndrome do not show any symptoms, some cases only inflict pain when the heel is pressed too tight on the floor or when the heel comes in contact with very rigid surfaces.
Heel pad syndrome diagnosis
If you have heel pain, it is crucial to approach a doctor for a proper diagnosis for your heel pad. A proper diagnosis might be able to provide you with a great treatment to recover fast.
- A qualified physician will take a prior medical history to attain a proper examination and treatment. Few other medical ailments such as arthritis, diabetes mellitus, lupus, and nerve damage might further add to heel pad syndrome. The physician will examine you in detail and find out the type, span, time, and severity of recurrence of pain due to this condition, and you should give them precise details of your condition to plan the treatment.
- After obtaining your complete medical history, the health care expert will perform a physical test of the feet for any noticeable abnormality or deformation in your heel. With this, they might find out the exact position of the pain by moving their fingers from the bottom of their heel to the upper side. At times, your heel bones are examined by pressing on your skin to monitor any anatomical abnormality in the bones of the sole.
- To examine the flexibility of your heel pad, some extra analysis is done, which covers the difference in the density or thickness of the heel sole when you are in standing, lying, and sitting positions. This is because heel pads which do not handle much weight will provide evidence to the doctor about the heel situation.
- If your heel pads remain stiff and hard, you have a problem compressing the heel, which provides the doctor an idea of little elasticity in the heel muscles. This little elasticity cannot support your bodyweight indicating you have heel pad syndrome.
- Further, an X-ray analysis will also be performed to exclude other medical concerns which have similar results to heel pad syndromes, for example plantar fasciitis or heel bone fracture.
- The clinical diagnostic techniques mentioned above are standard procedure. But, in case of uncertainty where these procedures do not provide a conclusive statement, ultrasound (US) or MRI might be performed as these are excellent and advanced diagnostic tools.
If the doctors can determine that you have heel pad syndrome, not other conditions, they will plan a suitable treatment to heal your heel pad.
Heel pad syndrome- Treatment

Heel pad syndrome could be healed by decent management and treatment options, and it is classified into two different methods- Conservative therapy and Innovative or non-conventional methods.
Conservative treatment for the heel pad syndrome
In the conservative treatment approach for heel pad syndrome, the basic aim is to manage the indications and symptoms by decreasing the inflammation and pain in the heel thus enhancing the essence of life. It does not involve the placement of all the lost fatty tissues again within the heel. It strives to preserve and defend the leftover fat and muscle tissues in your heel pad to limit further injury and lessen inflammation, which supports the natural healing manner in your heel sole.
This includes-
- Having Proper Rest: Whenever you sense this type of intense or mild pain in the heel, it is important to take a decent amount of rest. You must walk less, dodge heavy exercise and games, do not shoulder a heavy load, decrease your walking duration and standing time.
- Try icing of your feet: Icing of feet always has a great impact in decreasing the swelling and pain in the heel pad. After all, the restless or hectic activities that you perform might result in heel pain, so attempt to ice the feet for at least 10 to 20 minutes.
- Physical therapy or massage: Standard massage plans include recovery and restoration exercises for your ankle joints, leg, and feet. Massaging the soft tissue inside the heel is discovered to be an efficient method in reducing the discomfort in your injured heel pad.
- Soothing low-dye taping method: This method has been demonstrated to be effective in managing the heel pad syndrome, usually used in the therapy of another similar condition called plantar fasciitis, but study reports have stated that this a prominent tool in the heel pain syndrome as well. This technique is a helpful and convenient means mainly when done indoors where orthotics and your heel pads are less susceptible to damage, as it cushions your heel by improving the thickness of the fat layer in your heel pad.
- Usage of medicines: Several medicines such as analgesics (pain reliever) or anti-inflammatory drugs like Ibuprofen or Voltaren, may assist in reducing heel pain.
- Using Heel cups and orthotics- Heel cups are special shoe enclosures created to give heel comfort and cushioning. You might also find orthotic soles created to grant extra heel assistance or cushioning. Both- Heel cups and orthotics are present to be bought online and at many pharmacies near you.
Non-conventional treatment for heel pad syndrome
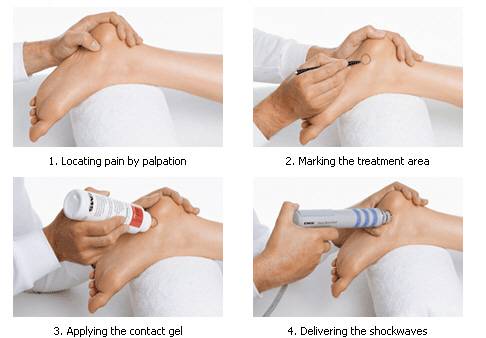
If the conventional methods given above do not present conclusive results or in few cases of heel pad syndrome or heel fat atrophy where no improvement is seen, these advanced techniques assist patients in relieving heel pain and heel fat pad syndrome.
This includes-
- Injectable therapy: several materials are utilized or practiced in form of injectables that help thicken all the shrunken or damaged parts of the heel pad, thus providing comfort and relief from pain.
- Fat transplantation and auto lipo-transplantation: This process is also called the grafting of the fat tissues or fat addition as it includes displacing the fatty tissues from one region of your body where it is abundant or in higher concentration to a different part, i.e., heel (in case of heel syndrome) where it is present in low concentration (the position of graft).
- Allografting: This is another or third method in this category, it is quite the same as autografting, but in this method, the source from where fat is taken is another individual and not your body part. The fat is taken from the donor and then grafted to the heel of the individual (recipient). The foreign nature of the fat cells of the giver can’t guarantee that the patient’s body will not deny it.
Treatment of another underlying deformity or abnormality: If heel pad syndrome is a result of an underlying deformation that exerts too much pressure and stress on your heel, it is fundamental to address this irregularity by operating it. Individuals suffering from diabetes mellitus usually state having claw toe deformities, other people have ankle or knee joint deformation problems, the treatment for such type of individuals is either traditional or surgical based upon the practitioner choice.
Prevention of heel pad syndrome
As we have explained above, several factors are present that contribute to the complication of heel pad syndrome. Some factors involved cannot be ignored or even operated, such as the aging process and genetics of the sufferers. However, other factors or causes can be neutralized with proper steps and choosing a healthy lifestyle.
- Wear fitting footwear that is tightly cushioned and grants support to your heel pad all the time you are performing some activities.
- In a time of performing a high-impact activity, wearing sports shoes that support your heel pad is highly important.
- Decreasing the intensity and duration of advanced workouts and heavy activities, such as running, prolonged standing, jogging, and jumping, ensure the fast recovery of your heel pad after the activities.
- Wearing bold high heels, particularly the one that is pointed, must be shunned, as these heels scatter the bodyweight roughly and put further pressure on your feet.
- Barefooted walking even around your home must be avoided, especially on rigid or hard surfaces.
- Check the strength, stability, and condition of the athletic shoes you wear regularly and try to replace them when you see any decline in their cushion.
- Maintain a healthy body weight to dodge heel pad syndrome.
The Bottom Line
Your heel pad is a dense and thick layer of fat tissue found on the feet in the rear section of your feet. Heel pad syndrome may develop if the heel pads lose all their thickness and elasticity.
It usually happens over time as a result of too much wear and tear, constant activities, holding extra weight, or an irregular weight distribution when people walk.
The principal sign of heel pad syndrome is intense pain or tenderness in the center of the heel, particularly when you try to stand for some time or walk. These signs are normally manageable with proper treatment.
This was all about heel pad syndrome and how you can follow the prevention tips to dodge developing such a condition.

